
The business software landscape is undergoing a seismic shift from traditional ownership to subscription-based models, driven by the growth of Software as a Service (SaaS). Companies are increasingly abandoning the conventional approach of purchasing and maintaining their own systems, finding it inefficient and costly. The growing preference for SaaS solutions reflects a desire for flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
The Shift From Ownership to Subscription
Maintaining and running proprietary software systems has become a significant financial burden for many businesses. Enterprises spend an average of 20-25 percent of their IT budgets on software maintenance, including updates, patches, and support.
This number does not account for the initial capital expenditure on software licenses and hardware, which can amount to millions of dollars. The costs of maintaining on-premises systems also include substantial IT staffing, often dedicated solely to managing these systems.
These financial commitments become roadblocks to growth and scalability. Companies must continually invest in infrastructure for technological advancements, diverting funds that could otherwise be used for innovation and expansion. Moreover, the complexity of managing these systems can lead to inefficiencies and increased downtime, further hampering business agility.
Rise of the Subscription Economy and Its Impact on Various Industries
The subscription economy has transformed how businesses and consumers access services. Popularized by companies like Netflix, Spotify, and Uber, the model offers predictable, ongoing expenses instead of large upfront costs.
This trend has extended into the business software realm, where SaaS solutions dominate. The global SaaS market, valued at $273.55 billion in 2023, is expected to grow to $1,228.87 billion by 2032.
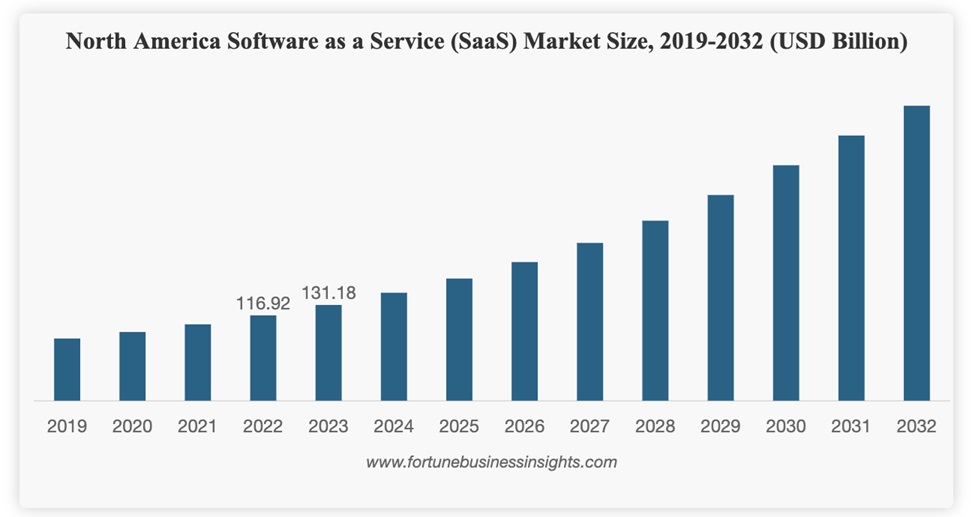
Image from Fortune Business Insights
This shift signifies a broader move toward operational flexibility and financial prudence.
The Benefits of SaaS for Businesses
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet or the cloud, eliminating the requirement for on-premises installations and maintenance. This model enables businesses to access the software on a subscription basis, paying monthly or annually, significantly lowering the initial investment.
SaaS providers manage all aspects of software management, including security, updates, and infrastructure, freeing businesses from the complexities of software maintenance.
Here are some of the advantages of adopting SaaS models:
Cost efficiency
SaaS reduces upfront costs compared to traditional software purchases. Instead of a large initial investment, businesses pay predictable, ongoing subscription fees. This model aligns expenses with usage, providing financial flexibility.
For example, building a basic video solution can cost around $110,000 in the first year, with maintenance costs. Scaling and support costs can add up to $312,000 per year for a more complex solution. However, video encoding costs on the cloud will be much cheaper. SaaS eliminates the cost of hardware and reduces IT maintenance expenses, enhancing cost efficiency.
Scalability and flexibility
SaaS solutions are inherently scalable, allowing businesses to adjust their subscriptions based on changing needs. Companies can easily modify their usage without significant disruptions, whether expanding operations or downsizing. This flexibility extends to subscription plans and features, enabling organizations to select options that best suit their requirements.
Accessibility and collaboration
SaaS applications are cloud-based, providing remote access from any device with an internet connection. This accessibility fosters collaboration among teams, regardless of their physical locations. Real-time updates and data sharing enhance productivity and streamline workflows.
Challenges and Considerations of SaaS Adoption
While SaaS adoption can improve business operations, it still comes with various areas for improvement.
Data security and privacy concerns
Storing confidential data in the cloud raises security and privacy concerns. Data breaches have severe consequences, including financial losses and reputational damage. Selecting reputable SaaS providers with robust security measures is crucial. Reports indicate that cloud exploitation increased by 95 percent in 2022, emphasizing the need for vigilant security practices.
Dependency on Internet connectivity
SaaS relies on stable internet connectivity. Disruptions can impact access to critical applications and data, affecting productivity. Businesses must implement strategies to mitigate this risk, such as backup internet connections and offline capabilities. Ensuring continuous access and productivity requires robust internet infrastructure and contingency plans.
Long-term costs and vendor lock-in
While SaaS offers cost advantages, long-term subscriptions can accumulate substantial expenses. Businesses must analyze the total cost of ownership and consider potential vendor lock-in. Organizations should negotiate flexible contracts and ensure data portability to avoid dependency on a single provider. By doing so, they can switch vendors or revert to traditional models if necessary.
Market Trends Driving SaaS Adoption
Let’s explore the industry trends that encourage the widespread adoption of SaaS.
Innovation and continuous improvement
The competitive SaaS market drives continuous innovation, resulting in frequent updates and new features. Providers leverage AI and machine learning to enhance software capabilities, offering businesses advanced tools for decision-making and automation. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 55 percent of SaaS offerings will incorporate AI functionalities, underscoring the trend toward intelligent, data-driven solutions.
Customer-centric business models
SaaS providers prioritize customer success and personalized experiences. Subscription models foster closer relationships, as providers are incentivized to ensure customer satisfaction and retention. This focus on customer-centricity leads to better support, tailored solutions, and ongoing value delivery.
Global expansion and market penetration
SaaS enables businesses to operate and compete globally. Providers offer localized solutions that cater to diverse markets and regulatory requirements. This global reach is necessary for companies looking to expand their footprint and tap into new opportunities. The ability to quickly deploy and scale SaaS solutions across geographies is a key advantage in today’s interconnected world.
The Future of Business Software: Predictions and Opportunities
How will business software evolve and change the landscape of business operations? Here are some predictions.
Emergence of hybrid models
Hybrid models that combine ownership and subscription elements are emerging. These models offer the flexibility of SaaS with the control of traditional software. Pay-per-use and modular solutions allow businesses to customize their software stack based on specific needs. According to IDC, hybrid cloud adoption is predicted to flourish at a CAGR of 22.12 percent through 2029, reflecting the trend toward mixed deployment strategies.
Increased customization and integration
The growth of APIs and third-party integrations drives increased customization of SaaS solutions. Businesses can tailor their software environments to meet unique requirements and enhance interoperability. Seamless workflows and integrated systems improve efficiency and user experience.
Sustainability and environmental impact
SaaS contributes to more sustainable business practices by reducing physical hardware requirements and energy consumption. Cloud-based solutions minimize the need for on-premises infrastructure, lowering carbon footprints.
The shift toward SaaS aligns with growing environmental consciousness and corporate sustainability goals. Cloud migrations can reduce carbon emissions by up to 98 percent, highlighting the environmental benefits of SaaS.
Navigating the Transition to SaaS
Understanding its benefits and challenges is crucial as businesses consider transitioning to SaaS. Evaluating software needs and selecting the right SaaS solutions can drive innovation and growth. By embracing SaaS, companies can enhance efficiency, collaboration, and scalability while navigating the evolving business software landscape.
The future of business software lies in the balance between ownership and subscription, and SaaS is at the forefront of this transformation.

