Like other alumni associations and interest groups, the Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Alumni association converged on Victoria Island, Lagos few days ago to deliberate on the issue of national importance. The gathering, which had scholars, professionals and public analysts in attendance was the 6th Biennial Lecture of the association. From the Keynote Speaker, Dr. Kingsley Fregene, to the Guest Speaker, Professor Ndubuisi Ekekwe, and the Vice Chancellor of the University, Professor Francis Eze, the theme of the conference “the pursuit of exponential development” was dissected through practical and empirical lenses.
The speakers walked the audience through linear and exponential growths and how they have been pursued around the world. From them and other existing sources, linear growth indicates the development of an object by the same rate in each time it takes to advance to a new position. In other words, it is a change in size that proceeds at the same rate over time. Exponential growth is an indication that a change is occurring when ‘the instantaneous rate of change of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself.’
The consensus among the speakers and the participants was that Nigeria needs to work on her policies and programmes towards economic development and growth because ‘the traditional growth strategies are grossly inadequate in addressing the daunting 21st century challenges.’ According to the Vice Chancellor of the institution, Nigeria had witnessed stunted growth over the decades, which has continued to be the bane of making millions remain in poverty and failed to place her on the league of developed nations.
Register for Tekedia Mini-MBA edition 19 (Feb 9 – May 2, 2026): big discounts for early bird.
Tekedia AI in Business Masterclass opens registrations.
Join Tekedia Capital Syndicate and co-invest in great global startups.
Register for Tekedia AI Lab: From Technical Design to Deployment (next edition begins Jan 24 2026).
Speakers and participants, once again, reminded Nigerian government and citizens about the consequences of population being grown exponentially while the economic growth is being achieved at snail pace. “As Nigeria’s population grows, there is need to embrace technologies, innovate on how we grow crops, add value to them and invent technologies to fight hunger and live a modern live,” the Vice-Chancellor stressed.
What the Numbers Say
From the practical lens to the empirical lens, the speakers and participants emphasized the need to look at what various economic numbers have implied for Nigeria in the last decade and still represent as the country moves to another decade. Professor Ekekwe believes that exponential growth hurdle is a matter of being an inventive society, not only an innovative one.
To buttress his stance, the renowned scholar and entrepreneur compared the United States of America and China using 2,000 years’ GDP constant price ($US billion). The comparison shows that China has been matching the USA’s constant prices growth rate in recent years. This was attributed to the country’s efforts to be an innovation society with the intent of advancing socially and economically.
Between 2014 and 2018, Nigeria and other countries in Africa and Asia had irregular constant GDP prices growth. Within the period, it was difficult for Nigeria and South Africa to have growth similar to what was recorded by the United States of America and China [see Exhibit 1-4 for the place of Nigeria among the select countries in Africa, Asia, America and Europe]. Going forward, Nigeria is likely not to be on the par with the two countries (USA and China) because the projected constant GDP prices indicate the irregular growth rate as from 2020 [see exhibit 2].
Exhibit 1: Nigeria among other countries within constant GDP Prices Growth 2014-2018
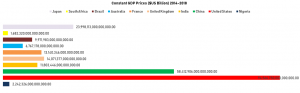
Exhibit 2: GDP Constant Prices ($US dollars) 1980-2024
Professor Ekekwe’s postulation was further analysed using select competitiveness indicators of Nigeria as studied by the World Economic Forum over the years to pinpoint specific issues preventing Nigeria from achieving exponential development and growth. Analysis reveals a number of results which require critical examination from the policymakers, scholars and professionals.
Analysis shows that Nigeria’s Global Competitiveness rankings within the government procurement of advanced technology products, the efficiency of the government spending, irregular payments and bribes, strength of investor protection and quality of overall infrastructure impacted the GDP constant prices growth between 2014 and 2018 negatively.
Exhibit 3: Comparison of Constant GDP Prices $US Billion I
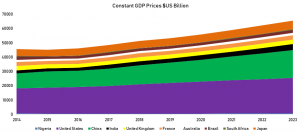
Exhibit 4: Comparison of Constant GDP Prices $US Billion II
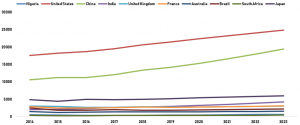
The results also indicate that poor and unsustainable tax policies and programmes, the difficulty in accessing loan and inadequate technological adoption by businesses denied Nigeria additional 45% of its GDP Constant Prices ($2,242,326,000,000,000.00) between 2014 and 2018. The severity of the select competitiveness indicators ensured that the constant GDP prices moved irrationally [see exhibit 5 where the coefficient correlation of the trend of the select global competitiveness indicators analysed along with the trend of the GDP Constant Prices ($US dollars) are presented].
The inconsistency was aided by the government failure to make the right decisions towards faster innovation, undocumented extra payments and bribes connected with imports and exports, public utilities, annual tax payment, awarding of public contracts and licenses and obtaining favourable judicial decisions.
The lack of efficiency in public fund spending, extremely underdeveloped of transport, communications and energy infrastructure, the difficulty in obtaining bank loans, low capacity for investor protection, the impact of taxes on the readiness to invest and low adoption of the latest technologies by businesses were also the blocks that prevented the country from realizing substantial constant GDP prices. These results suggest that the country needs new strategies and tactics for exponential growth as espoused by the keynote and guest speakers.

In contrary to the position of the speakers and participants at the conference, analysis reveals that it was much easier for companies to obtain information about changes in government policies and regulations that affected their activities, for start-up entrepreneurs with innovative but risky projects to obtain equity funding and that intellectual property was protected to some degree from 2014 to 2018. It was also found that there were business clusters across the country and to some extent the Nigerian companies had some level of competitive advantage globally. However, the competitiveness was mixed between low labour cost and having unique products and processes.
Exhibit 5: Trend of GDP Constant Prices ($US dollars) and Select Global Competitiveness Indicators Correlation
Steps to Exponential Development
From the insights, it is obvious Nigeria needs to improve on policies and programmes that will ensure investor protection, competitive advantage, government procurement of advanced technological products, venture capital availability, enabling environment for businesses operating at different clusters across the country. These among others are essential for Nigeria’s exponential growth attainment. To be at par with the United States of America, the United Kingdom, China, Japan, India and others, Nigeria needs three categories of mindset, according to the keynote speaker.
The mindsets evolved from the development attitude index, which aims at reorienting Nigerian government and her people to the right approaches to exponential growth fulfillment. Based on the keynote speaker’s analysis and observation, it is glaring that Nigeria needs additive, multiplicative and combinatorial mindsets at different stages towards the exponential growth arena. Based on the results presented on exhibit 5, Nigeria would have attained more than what she had for the constant GDP prices between 2014 and 2018 if additive and multiplicative mindsets have been adopted while making or developing and executing policies and programmes. This is premised on the fact that at one stage to the other some select GCI indicators were constantly in movement with the constant GDP prices, which requires additive mindset. On the other hand, the select GCI indicators increased as the trend of the constant GDP prices increased, which called for multiplicative mindset.
As Nigeria continues to aspire to be exponential development and growth, the keynote speaker warned that having the mindsets are not enough, governments, businesses and people must have ‘competition scale thinking’. Within the scale, there must be evolutionary, competitive and revolutionary before the needed exponential growth could be achieved. There must be enabling public policy, retrofit, wide-aperture of human capital and clustering beyond borders within competitive, evolutionary, revolutionary and exponential developments respectively.
Exhibit 6: Factors Restricting Nigeria’s Movement to Exponential Development Stage

Making the Steps Successful
The convergence to exponential development is not always linear. Nigeria must be ready to operate simultaneously in all four states of development. In addition to the previous suggestions, a number of frictions must be fixed by the government and relevant stakeholders, according to Professor Ndubuisi Ekekwe.
Professor Ekekwe calls for germane knowledge development and entrepreneurial capitalism. The call for knowledge-driven processes and production further reinforced the need to do every task related to input and output using knowledge and skills. On the entrepreneurial capitalism, he stressed the need for governments to make environment ideal for those who are ready to utilize knowledge and pioneer new things to fix existing frictions across the sectors.
To ease the effects on taxes on the incentive to invest, establishing and operating business, he stresses the need to fix the tax fold to enhance capital availability and advocates smart tax policy to encourage more people to inject more capital into universities. Though, a positive connection was discovered for the intellectual property right protection and the constant GDP prices between 2014 and 2018, Professor Ekekwe believes that the right must be strengthened, while the fraud in the government procurement system must be eliminated using advanced technologies. Frictions in the agriculture, especially the land rights and healthcare sectors equally need attention with regenerative distributive policies that work to regenerate capital assets.
Exhibit 7: Frictions and Nigeria’s Movement to Exponential Development